E-filing of Income Tax Returns in India (FY 2022-23, AY 2023-24) is mandatory for various income groups. Filing income tax is a responsibility for every Indian citizen, now made easier with online technology. The process on the official website involves selecting the right ITR form, ranging from ITR 1 to ITR 7, each tailored for different taxpayer categories. Accuracy is crucial, as any errors or omissions can delay the filing.
The deadline for filing without late fees was July 31, 2023.
Taxpayers are required to provide necessary documents for the process. Key documents vary for employees and business owners, including PAN, Form 16, and financial statements. Benefits of e-filing include faster refunds and improved credit scores. Special provisions apply to senior citizens and specific tax slabs are outlined for them.
Although, the Belated Return for the (FY 2022-23, AY 2023-24) can be filed upto 31st December 2023.
Applicability: – Salaried resident individuals having income up to Rs 50 lakh.
Income Source: – Salary, Pension, Single House Property and Other Sources.
Applicability: – Individuals (Resident and NRI’s) having total income of more than 50 lakhs.
Income Source: – Salary, Pension, more than One House Property and Other Sources.
Applicability: – Individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) whose total income includes Income from a profession or business carried under a proprietorship firm.
Income Source: – Business or profession, Director of the company, Partner of Firm, Salary, more than One House Property, Other Sources & Capital Gain.
Applicability: – Individuals and Hindu Undivided Family having income from business which has presumptive income under section 44AD, 44ADA and 44AE
Income Source: – Presumptive Income (Business Income), Salary Income, House Property and other Sources as per Section 44AD, Section 44ADA and Section 44AE.
Applicability: – Firms, LLPs, Associations of Persons (AOPs), BOIs, Artificial Judicial Persons, Cooperative Societies and Local Authorities
Income Source: – House Property, Capital Gain, Business & Profession & Other Sources.
Applicability: – All companies registered under the Companies Act 2013/1956. Companies other than companies claiming exemption under section 11 must furnish their income tax return in ITR-6 Form.
Income Source: – House Property, Capital Gain, Business & Profession & Other Sources.
Applicability: – Charitable Trusts, Religious Trusts, Political Parties, Scientific research institution, University, college or other institution.
Income Source: – House Property, Capital Gain, Business & Profession & Other Sources.
The Table below shows the Income Tax Slabs applicable for the F.Y. 2023-24, as per NEW TAX REGIME. The new tax slabs are as per the approval of the Finance Budget 2023. The new tax regime slabs-
| Tax Slab | Rates |
|---|---|
| Up to Rs. 3,00,000 | NIL |
| Rs. 300,000 to Rs. 6,00,000 | 5% on income which exceeds Rs 3,00,000 |
| Rs. 6,00,000 to Rs. 900,000 | Rs 15,000 + 10% on income more than Rs 6,00,000 |
| Rs. 9,00,000 to Rs. 12,00,000 | Rs 45,000 + 15% on income more than Rs 9,00,000 |
| Rs. 12,00,000 to Rs. 1500,000 | Rs 90,000 + 20% on income more than Rs 12,00,000 |
| Above Rs. 15,00,000 | Rs 150,000 + 30% on income more than Rs 15,00,000 |
| Tax Slab | Rates |
|---|---|
| Rs. 3 lakhs | NIL |
| Rs. 3 lakhs - Rs. 5 lakhs | 5.00% |
| Rs. 5 lakhs - Rs. 10 lakhs | 20.00% |
| Rs. 10 lakhs and more | 30.00% |
| Tax Slab | Rates |
|---|---|
| Rs. 0 - Rs. 5 lakhs | NIL |
| Rs. 5 lakhs - Rs. 10 lakhs | 20.00% |
| Above Rs. 10 lakhs | 30.00% |
| Particulars | Old Tax Regime | New Tax Regime |
|---|---|---|
| Company opts for section 115BAB (not covered in section 115BA and 115BAA) & is registered on/after October 1, 2019 and has started manufacturing on/before 31st March 2024 | - | 15% |
| Company opts for Section 115BAA, where the total income of a company has been calculated without claiming specified deductions, exemptions, incentives, and additional depreciation | - | 22% |
| Company opts for section 115BA registered on/after March 1, 2016, and is in the manufacture of any article or thing and does not claim a deduction as specified in the section | - | 25% |
| Turnover/gross receipt of the company is less than Rs. 400 crores in the previous year | 25% | 25% |
| Other Domestic Company | 30% | 30% |
Health & Education Cess Rate – 4%
Surcharge Rate-
A partnership firm or an LLP is taxable at 30%
Note –
The HUF and Individual tax slab applicable as per New Tax Regime are-
| Slab | New Tax Regime (Before Budget 2023 - until 31 March 2023) | New Tax Regime (After Budget 2023 - From 01 April 2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Rs. 0 to Rs. 2,50,000 | NIL | NIL |
| Rs. 2,50,000 to Rs. 3,00,000 | 5% | NIL |
| Rs. 3,00,000 to Rs. 5,00,000 | 5% | 5% |
| Rs. 5,00,000 to Rs. 6,00,000 | 10% | 5% |
| Rs. 6,00,000 to Rs. 7,50,000 | 10% | 10% |
| Rs. 7,50,000 to Rs. 9,00,000 | 15% | 10% |
| Rs. 9,00,000 to Rs. 10,00,000 | 15% | 15% |
| Rs. 10,00,000 to Rs. 12,00,000 | 20% | 15% |
| Rs. 12,00,000 to Rs. 12,50,000 | 20% | 20% |
| Rs. 12,50,000 to Rs. 15,00,000 | 25% | 20% |
| More than Rs. 15,00,000 | 30% | 30% |
Under the new tax regime of taxation, the taxpayers can avail of an option to opt for one of the following-
To pay tax at lower rates according to the New Tax Regime of taxation on the condition that they refrain from specific exemptions (permissible) and deductions under income tax.
To continue paying the taxes under the existing income tax rates. The taxpayer can avail of exemptions and rebates by opting into the old regime and paying tax at the existing higher rate.
The taxpayers who have opted for the new tax regime will have to forgo some deductions and exemptions that are available in the old tax regime of taxation.
The old income tax slabs (old tax regime) and the tax rates for Individuals and HUF below the age of 60 years and NRIs under the old tax regime are as below:
| Income Tax Slab | Tax Rates |
|---|---|
| Up to Rs 2,50,000* | NIL |
| Rs 2,50,001 - Rs 5,00,000 | 5% |
| Rs 5,00,001 - Rs 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Above Rs 10,00,000 | 30% |
Surcharge
Note – As per the approved Finance Budget 2023, the highest surcharge rate of 37% has been decreased to 25% under the New Tax Regime (i.e., Applicable w.e.f. 01.04.2023)
| Old Tax Regime | New Tax Regime | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Slabs | Old Tax Rates | Tax Slabs | New Tax Rates |
0 – 2.5 Lakh | 0% | 0 - 3 Lakh | 0% |
2.5 Lakh – 5 Lakh | 5% | 3 Lakh – 6 Lakh | 5% |
5 Lakh – 10 Lakh | 20% | 6 Lakh - 9 Lakh | 10% |
10 Lakh and above | 30% | 9 Lakh - 12 Lakh | 15% |
| - | - | 12 Lakh - 15 Lakh | 20% |
| - | - | 15 Lakh and above | 30% |
The old regime has multiple tax slabs with higher rates, while the new regime offers lower rates with more slabs.
The old regime allows various deductions and exemptions, which are mostly not available under the new regime.
The new regime aims for simpler tax calculations with fewer exemptions, whereas the old regime offers more avenues to reduce taxable income.
The old regime may be more beneficial for those with high investments and expenses qualifying for deductions, whereas the new regime could be better for those with fewer deductions.
Taxpayers have the option to choose between the two regimes based on which is more advantageous for their situation.
| Key Points | Old Tax Regime | New Tax Regime |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Slabs | Offers graduated tax slabs ranging from 0% to 30%, with additional surcharges for high-income earners. | Features simplified slabs of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 30%, eliminating deductions and exemptions except for specified ones like home loan interest and standard deduction. |
| Deductions and Exemptions | Allows a plethora of deductions and exemptions on investments, medical expenses, education expenses, etc., reducing taxable income. | Offers no deductions or exemptions except for those mentioned above. |
| Tax Rates | Generally has higher marginal tax rates, but deductions and exemptions can significantly reduce the effective tax rate. | Offers lower marginal tax rates compared to the old regime, especially in lower income brackets. However, the lack of deductions may result in a higher tax burden for individuals making extensive use of them in the old regime. |
| Compliance | Requires maintaining detailed records for deductions and exemptions, leading to higher paperwork and compliance burden. | Is simpler to comply with due to no deductions or exemptions, requiring minimal paperwork and record-keeping. |
| Suitability | Generally benefits individuals with high income and significant deductible expenses. | May be advantageous for salaried individuals, pensioners, and those with lower incomes or limited deductible expenses. |
Other points to consider:
In conclusion, both regimes have their pros and cons. The “better” regime depends on your individual circumstances and income profile. Thoroughly evaluate your financial situation and consult a professional if needed to make an informed decision about which regime best suits your needs.
Form 26AS is a consolidated tax statement issued by the Income Tax Department of India. It serves as a record of the tax deducted at source (TDS) on an individual’s income, tax collected at source (TCS), and details of other taxes paid. Additionally, it includes information on high-value transactions, advance tax, and self-assessment tax payments. This form is crucial for verifying tax credits while filing income tax returns and is accessible online through the taxpayer’s account on the e-filing website of the Income Tax Department.
Form AIS (Annual Information Statement) and TIS (Taxpayer Information Summary) in India are comprehensive documents introduced by the Income Tax Department. AIS provides detailed information on financial transactions of a taxpayer for a particular financial year, including savings, investments and expenditures. It’s more detailed than Form 26AS. TIS, on the other hand, is a simplified summary derived from AIS, offering an overview of the taxpayer’s reported transactions. These forms assist in ensuring accurate income tax return filing and facilitate transparency in financial transactions.
Form AIS and TIS are key documents from India’s Income Tax Department:
Aadhaar Card
PAN Card
Bank Statement
Form 16 (for Salaried Person)
House Property Income
Capital Gain Report
Investment Details
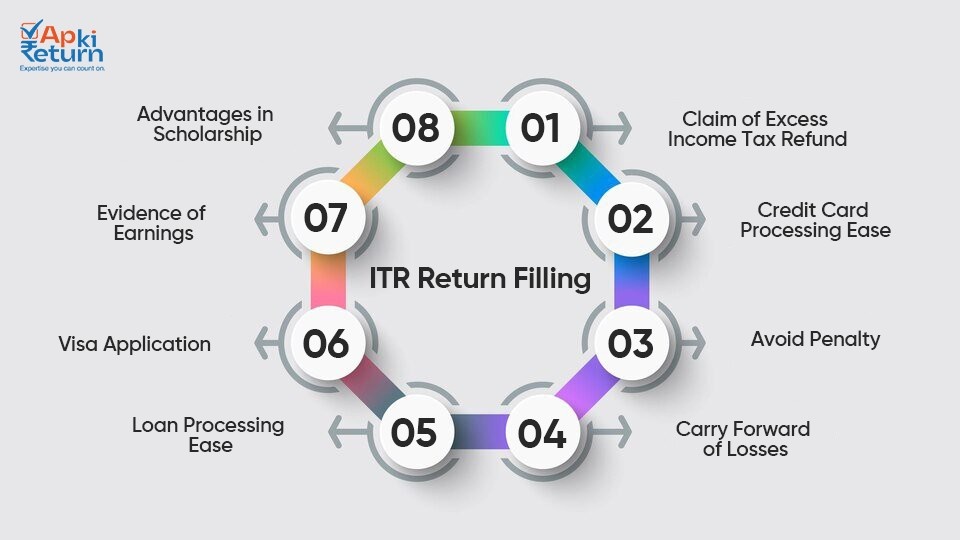
An Income Tax Return (ITR) is a form used by taxpayers to declare their income, deductions and tax liability to the government. It serves as a record of one’s income and taxes paid.
Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), companies, and other entities earning income in India are required to file an Income Tax Return if their income exceeds the prescribed threshold limit.
The due date for filing Income Tax Returns varies depending on the taxpayer’s category and the type of income. For individuals, the usual due date is July 31st, but it can be extended by the government.
The Income Tax Department has different forms (ITR-1 to ITR-7) for various categories of taxpayers. The choice of form depends on the source and amount of income.
Taxpayers can file their returns online through the official Income Tax Department website or other authorized e-filing portals. Offline filing is also an option using the appropriate ITR form.
Commonly required documents include PAN card, Aadhaar card, Form 16 (for salaried individuals), bank statements, investment details and other supporting documents for income and deductions claimed.
Yes, taxpayers can file a belated return after the due date, but there might be penalties and interest applicable. It’s advisable to file the return within the stipulated time to avoid these extra charges.
Gross Total Income is the total income before deductions under various sections, while Total Income is the income after deductions. Total Income is the basis for calculating tax liability.
Yes, linking Aadhaar with PAN is mandatory for filing Income Tax Returns. It helps in preventing tax evasion and ensures a unique identification for taxpayers.
Taxpayers can check the status of their filed returns on the official Income Tax Department website using their PAN and acknowledgment number. The status will indicate whether the return has been processed or is under scrutiny.

We proudly announce our new website packed with updated data, resources, and valuable information